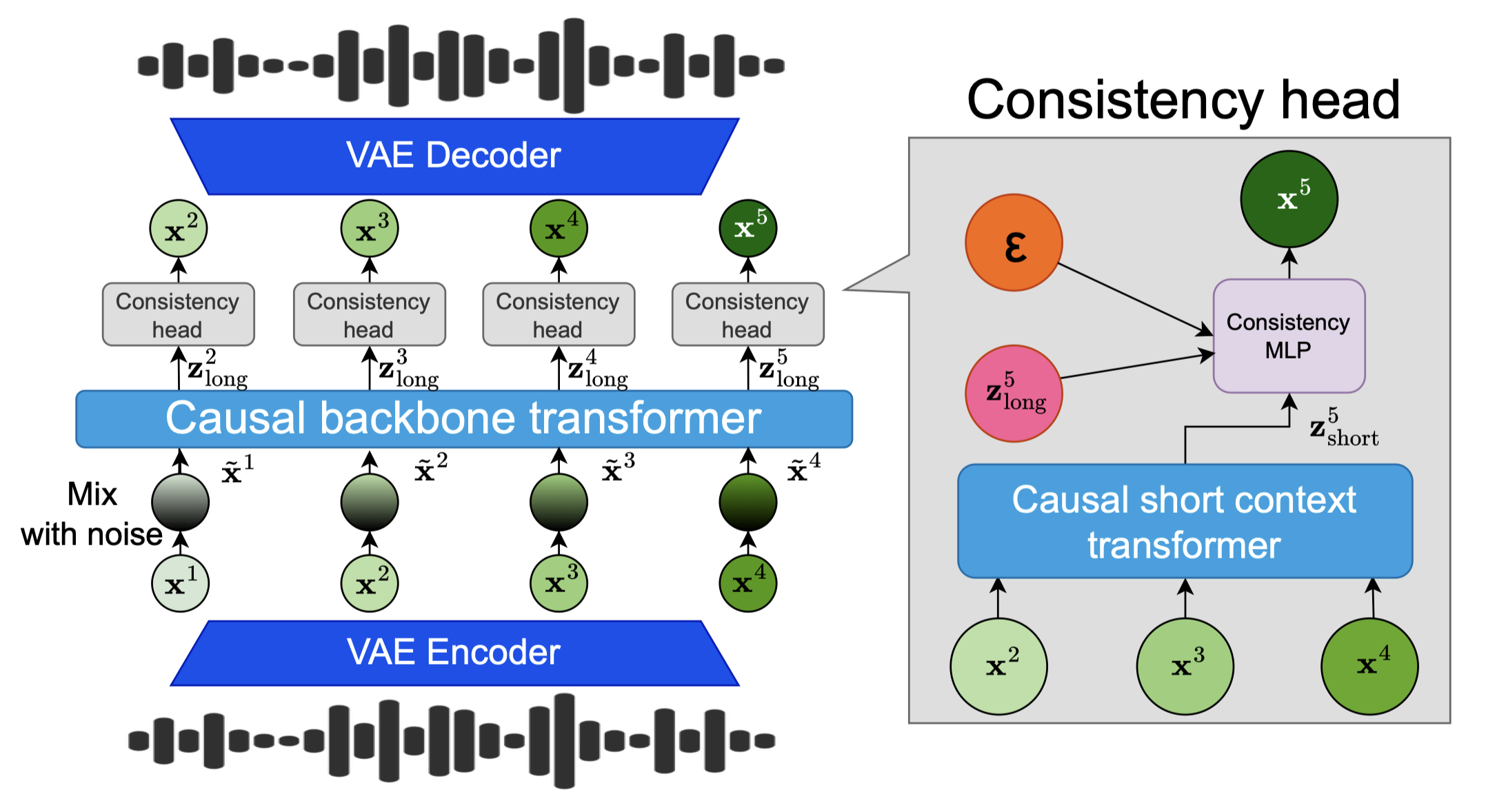

Audio Language Models (ALM) have emerged as the dominant paradigm for speech and music generation by representing audio as sequences of discrete tokens. Yet, unlike text tokens, which are invertible, audio tokens are extracted from lossy codecs with a limited bitrate. As a consequence, increasing audio quality requires generating more tokens, which imposes a trade-off between fidelity and computational cost. We address this issue by studying Continuous Audio Language Models (CALM). These models instantiate a large Transformer backbone that produces a contextual embedding at every timestep. This sequential information then conditions an MLP that generates the next continuous frame of an audio VAE through consistency modeling. By avoiding lossy compression, CALM achieves higher quality at lower computational cost than their discrete counterpart.
On this webpage, we show some results of our speech model as well as our music models. We illustrate as well the ablation study of the paper with some music samples.
This section presents examples of text-to-speech generation on the Librispeech clean test set. The samples from DiTAR were picked from their webpage. The audios have not been cheripicked. For DSM and F5TTS we generated the samples from the public code. Our CALM model uses only
| Prompt | Ground Truth | F5TTS (NFE=32) | DSM (16 RVQ) | DiTAR (NFE=10) | CALM (NFE=1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
This section presents music generated with a CLAP conditioning that are retrained on our dataset with the same backbone size (1.35B). The reference audio is encoded using CLAP, and we compare three models which are:
| Conditioning | MusicGen | 32 RVQ RQ-Transformer | Consistency CALM with 4 steps |
|---|---|---|---|
This section presents music generated from textual prompts using our three models trained with the CLAP conditioner:
| Text Prompt | MusicGen | 32 RVQ RQ-Transformer | Consistency CALM (4 steps) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Relaxing jazz music with saxophone | |||
| Dreamy ambient soundscape with airy pads | |||
| Energetic drum-and-bass with fast breakbeats | |||
| Hypnotic minimal techno with deep kick, subtle hi-hats, and evolving textures. | |||
| RnB song with vocals and piano | |||
| Warm lo-fi hip-hop beat with piano | |||
| Epic orchestral score with rising strings and triumphant brass. | |||
| A classic reggae song |
This section presents speech samples generated using a 3-second prompt. Key details of the setup and results include:
| Prompt | RQ-Transformer 8 RVQ temp=0.8 (baseline) |
CALM Consistency 1 Step temp=0.8 |
CALM Consistency 1 Step temp=1.0 |
RQ-Transformer 8 RVQ temp=1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
We compare our music generation models, all of which use a backbone with 1.35B parameters (from MusicGen Medium):
| Prompt | RQ-Transformer 32 RVQ (baseline) FAD: 1.06 | CALM TrigFlow 100 steps FAD: 0.64 | CALM Consistency 4 steps FAD: 0.71 | CALM Consistency 1 step FAD: 0.83 | Retrained MusicGen FAD: 1.72 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
We illustrate here the ablation study of our paper in order to show the importance of each component of our model. We showcase it on Music Generation with CALM Consistency 4 steps. All the models have been trained 300k steps instead of 500k steps.
| Prompt | Our Model | Without Noise Aug., Short Context Transformer, Head Batch Mult. | Without Short Context Transformer | Without Noise Aug. | Without Head Batch Mult. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|